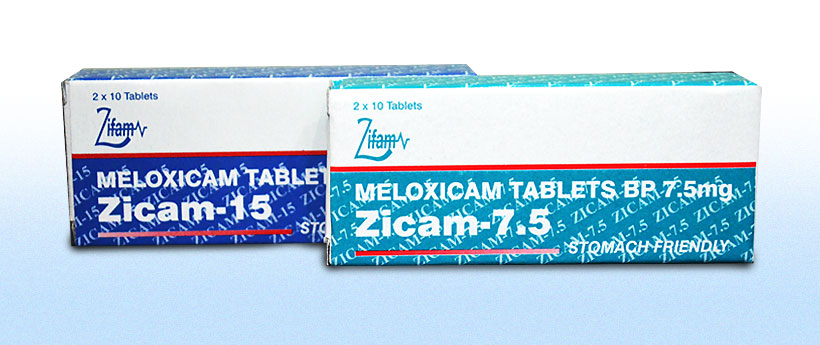
Zicam7.5/15
- ENG
- မြန်မာ
COMPOSITION:
ZICAM 7.5 – Each Uncoated Tablet Contains:
Meloxicam BP 7.5 mg
ZICAM 15 – Each Uncoated Tablet Contains:
Meloxicam BP 15 mg
PHARMACOLOGICAL PROPERTIES:
PHARMACODYNAMICS:
Pharmacotherapeutic group: Non steroidal anti-inflammatory agents, oxicams.
Meloxicam is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) of the oxicam family, with anti-inflammatory, analgesic and antipyretic properties.
The anti-inflammatory activity of meloxicam has been proven in classical models of inflammation. As with other NSAID, its precise mechanism of action remains unknown. However, there is at least one common mode of action shared by all NSAID (including meloxicam): inhibition of the biosynthesis of prostaglandins, known inflammation mediators.
PHARMACOKINETICS:
Absorption
Meloxicam is well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, which is reflected by a high absolute bioavailability of 89% following oral administration (capsule).
Tablets, oral suspension and capsules were shown to be bioequivalent.
Following single dose administration of meloxicam, mean maximum plasma concentrations achieved within 2 hours for the suspension and within 5-6 hours with solid oral dosage forms (capsules and tablets).
With multiple dosing, steady state conditions were reached within 3 to 5 days. Once daily dosing leads to drug plasma concentrations with a relatively small peak-trough fluctuation in the range of 0.4 – 1.0 g/ml for 7.5 mg doses and 0.8 – 2.0 pg/ml for 15 mg doses, respectively (cmin and cmax at steady state, respectively). Maximum plasma concentrations of meloxicam at steady state, are achieved within five to six hours for the tablet, capsule and the oral suspension, respectively.
Extent of absorption for meloxicam following oral administration is not altered by concomitant food intake or the use of inorganic antacids.
Distribution
Meloxicam is very strongly bound to plasma proteins, essentially albumin (99%). It penetrates Into synovial fluid to give concentrations approximately half of those in plasma. Volume of distribution is low, l.e. approx. 11 L. Inter-individual varlation is the order of 30-40%.
Biotransformation
Meloxicam undergoes extensive hepatic biotransformation. Four different metabolites of Meloxicam were identified in urine, which are all pharmacodynamically inactive. The major metabolite, 5′-carboxymeloxicam(60% of dose), is formed by oxidation of an intermediate metabolite 5° hydroxymethyl meloxicam, which is also excreted to a lesser extent (9% of dose):
In vitro studies suggest that CYP 2C9 plays an important role in this metabolic pathway, with a minor contribution from the CYP 3A4 isoenzyme. The patient’s peroxidase activity is probably responsible for the other two metabolites, which account for 16% and 4% of the administered dose respectively.
Elimination
Meloxicam is excreted predominantly in the form of metabolites and occurs to equal extents in urine and faeces. Less than 5% of the daily dose is excreted unchanged in faeces, while only traces of the parent compound are excreted in urine. The mean elimination half-life is about 20 hours. Total plasma clearance amounts on average 8 mL/min.
Elderly:
Mean plasma clearance at steady state in elderly subjects was slightly lower than that reported for younger subjects.
INDICATIONS:
Zicam 7.5/15 is indicated for the treatment of
- Short-Term Symptomatic Treatment of Exacerbations of Osteoarthritis.
- Long-Term Symptomatic Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis or Ankylosing Spondylitis.
CONTRAINDICATIONS:
Zicam 7.5/15 is contra-indicated in the following situations:
- Third trimester of pregnancy
- Children and adolescents aged less than 16 years;
- Hypersensitivity to meloxicam or to any of the excipients in this formulation or hypersensitivity to substances with a similar action, e.g. NSAIDs, aspirin. Meloxicam should not be given to patients who have developed signs of asthma, nasal polyps, angioneurotic edema or urticaria following the administration of aspirin or other NSAIDs;
- History of gastrointestinal bleeding or perforation, related to previous NSAIDs therapy:
- Active, or history of recurrent peptic ulcer/haemorrhage (two or more distinct episodes of proven ulceration or bleeding)
- Severely impaired liver function
- Non-dialysed severe renal failure
- Gastrointestinal bleeding, history of cerebrovascular bleeding or other bleeding disorders;
- Severe heart failure.
- Meloxicam is contraindicated in treatment of perioperative pain after coronary artery bypass surgery (CABG)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS:
Undesirable effects may be minimised by using the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration necessary to control symptoms.
The recommended maximum daily dose should not be exceeded in case of insufficient therapeutic effect, nor should an additional NSAID be added to the therapy because this may increase the toxicity while therapeutic advantage has not been proven. The use of Meloxicam Tablets with concomitant NSAIDs Including cyclooxygenase-2 selective inhibitors should be avoided.
Meloxicam Tablets is not appropriate for the treatment of patients requiring relief from acute pain.
In the absence of improvement after several days, the clinical benefit of the treatment should be reassessed.
Any history of oesophagitis, gastritis and/or peptic ulcer must be sought in order to ensure their total cure before starting treatment with meloxicam.
Attention should routinely be paid to the possible onset of a recurrence in patients treated with meloxicam and with a past history of this type
Meloxicam tablets may be associated with a small increased risk of heart attack or stroke. Any risk Is more likely with high doses and prolonged treatment. Do not exceed the recommended dose or duration of treatment.
Discuss your treatment with your doctor or pharmacist if you have heart problems, have previously had a stroke or you think you might be at risk of conditions such as high blood pressure, diabetes or high cholesterol, or if you are a smoker.
INTERACTIONS:
Following medicine should avoided while on therapy of Zicam 7.5/15 mg any other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), including aspirin;
- medicines to prevent blood clotting, such as warfarin;
- medicines lo break down blood clots;
- medicines lo treat high blood pressure;
- oral corticosteroids;
- cyclosporin;
- any diuretic medicine (your doctor may monitor your kidney function if you are taking diuretics):
- lithium, used to treat mood disorders;
- selective serotonin re-uptake inhibitors, used in the treatment of depression;
- methotrexate;
- Colestyramine:
- you use an Intraulerne conlraceplive device (UD), Usually known as a coil
ACE-Inhibitors
NSAIDs may diminish the antihypertensive effect of ACE-inhibitors, This interaction should be given consideration in patients taking Meloxicam concomitantly with ACE-inhibitors.
Aspirin
When Meloxicam is administered with aspirin (1000 mg three times daily) to healthy volunteers, an increase in the AUC (10%) and Cmax. (24%) of Meloxicam was noted. The clinical significance of this interaction is not known; however, as with other NSAIDs concomitant administration of Meloxicam and aspirin is not generally recommended because of the potential for increased adverse effects.
Diuretics
Clinical studies, as well as post marketing observations, have shown that NSAIDs can reduce the natriuretic effect of furosemide and thiazides in some patients.
This response has been attributed to inhibition of renal prostaglandin synthesis, However, studies with furosemide agents and Meloxicam have not demonstrated a reduction in natriuretic effect.
Furosemide single and multiple dose pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics are not affected by multiple doses of Meloxicam. Nevertheless, during concomitant therapy with Meloxicam, patients should be observed closely for signs of renal failure, as well as to ensure diuretic efficacy.
Lithium
In a study conducted in healthy subjects, mean pre-dose lithium concentration and AUC were increased by 21% in subjects receiving lithium doses ranging from 804 to 1072 mg twice daily with Meloxicam 15 mg every day as compared to subjects receiving lithium alone. These effecis have been attributed to inhibition of renal prostaglandin synthesis by Meloxicam. Closely monitor patients on lithium treatment for signs of lithium toxicity when Meloxicam is introduced, adjusted, or withdrawn.
Methotrexate
NSAIDs have been reported to competitively inhibit methotrexate accumulation in rabbit kidney slices. Therefore, NSAIDs may reduce the elimination of methotrexate, thereby enhancing the toxicity of methotrexate. Caution is exercised when Meloxicam is administered concomitantly with methotrexale.
Cyclosporine
Meloxicam, like other NSAIDs, may affect renal prostaglandins, thereby altering the renal toxicity of certain drugs. Therefore, concomitant therapy with Meloxicam may increase cyclosporine’s nephrotoxicity. Caution is required when Meloxicam is administered concomitantly with cyclosporine.
Warfarin:
The effects of warfarin and NSAIDs on GI bleeding are synergistic, such that users of both drugs together have a risk of serious GI bleeding higher than users of either drug alone. Monitor anticoagulant activity, particularly in
the first few days after initiating or changing Meloxicam therapy in patients
receiving warfarin or similar agents, since these patients are at an increased risk of bleeding than with the use of either drug alone.
PREGNANCY AND LACTATION:
Zicam 7.5/15 is not recommended for use by women who are pregnant or breast-feeding.
Children (under 16 years old)
This medicine must not be given to children under 16years old.
Driving and using machinery
Do not drive or operate machinery until you know how Meloxicam tablets affect you. If the tablets make you feel light-headed, dizzy or drowsy, or cause blurred vision, do not drive or operate machinery.
DOSAGE AND DIRECTIONS FOR USE:
If you forget to take your tablet
Never take two doses on the same day to make up for one you have missed.
Take your usual dose the next day.
Rheumatoid Arthritis and Ankylosing Spondylitis:
The usual dose is 15 mg as a single dose. A dose of 7.5 mg daily is recommended for long term treatment of elderly.
Exacerbation Osteoarthritis:
The usual dose is 7.5 mg. Increase if necessary to a maximum of 15 mg dally given as a single dose.
Dosage in special situations:
In dialysis patients with severe renal failure: The dose should not exceed 7.5 mg per day. In patients with mild to moderate renal impairment (creatinine clearance of greater than 25 mL/min): The dose should not exceed 7.5 mg per day.
ROUTE OF ADMINISTRATION: Oral
SIDE-EFFECTS:
Common side effects
Difficulty in breathing, swelling of face, lips, tongue or throat.
Serious side effect:
Chest pain, weakness, shortness of breath, slurred speech, problems with vision or balance.
Black, bloody, or tarry stools.
Coughing up blood or vomit that looks like coffee grounds.
Swelling or rapid weight gain
Urinating less than usual or not at all.
Nausea, upper stomach pain, itching, loss of appetite, dark urine, clay-colored stools, jaundice (Yellowing of skin or eyes).
Skin rash, bruising, severe tingling, numbness, pain, muscle weakness.
Severe reaction- fever, sore throat, swelling in your face or tongue, burning in your eyes, skin pain, followed by a red or purple skin rash that spreads (especially in the face or upper body) and causes blistering and peeling.
OVERDOSAGE
Symptom
Symptoms following acute NSAID overdose are usually limited to lethargy, drowsiness, nausea, vomiting and epigastric pain, which are generally reversible with supportive care. Gastrointestinal bleeding can occur, Severe poisoning may result in hypertension, acute renal failure, hepatic dysfunction, respiratory depression, coma, convulsions, cardiovascular collapse and cardiac arrest. Anaphylactoid reactions have been reported with therapeutic ingestion of SAID and may occur following an overdose.
Treatment:
Patients should be managed with symptomatic and supportive care following an NSAID overdose. Accelerated removal of meloxicam by 4 g oral doses of cholestyramine given three times a day was demonstrated in a clinical trial.
PRESENTATION:
Blister pack of 5 x 2 x 10 Tablets
STORAGE:
Store below 30°C. Protect from light and moisture;
Keep medicine away from children
Updated on 9/Feb/2024