Urocalm 5/10
- ENG
- မြန်မာ
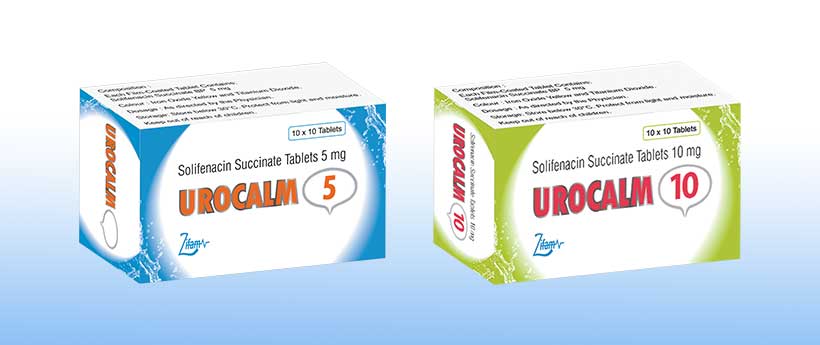
UROCALM 5/10
Solifenacin Succinate Tablets 5/10 mg
COMPOSITION
UROCALM 5
Each Film-Coated Tablet Contains:
Solifenacin Succinate BP 5 mg
UROCALM 10
Each Film-Coated Tablet Contains:
Solifenacin Succinate BP 10 mg
Product Description
UROCALM 5: Yellow coloured, circular, biconvex film coated tablets plain on both sides.
UROCALM 10: Pink coloured, circular, biconvex film coated tablets plain on both sides.
Indications and Usage
UROCALM is a muscarinic antagonist indicated for the treatment of overactive bladder with symptoms of unintentional loss of urine (urinary incontinence) urgency, and urinary frequency.
Pharmacological properties
Mechanism of Action
Solifenacin is a competitive, specific cholinergic-receptor antagonist.
Muscarinic receptors (M3) play an important role in several major cholinergically mediated functions, including contractions of urinary bladder smooth muscle and stimulation of salivary secretion. solifenacin reduces smooth muscle tone in the bladder, allowing the bladder to retain larger volumes of urine and reducing the number of incontinence episodes.
Other special populations
Elderly
No dosage adjustment based on patient age is required.
Paediatric
The pharmacokinetics of solifenacin has not been established in Paediatric children and adolescents.
Gender
The pharmacokinetics of solifenacin are not influenced by gender.
Race
The pharmacokinetics of solifenacin are not influenced by race.
Renal impairment
The AUC and Cmax of solifenacin in mild and moderate renally impaired patients, was not significantly different from that found in healthy volunteers. Pharmacokinetics in patients undergoing haemodialysis have not been studied.
Hepatic Impairment
In patients with moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh score of 7 to 9) the Cmax is not affected, AUC increased with 60% and t1/2doubled. Pharmacokinetics of solifenacin in patients with severe hepatic impairment have not been studied.
Recommended Dosage and Administration
Adults, Including the elderly
The recommended dose is 5 mg solifenacin succinate once daily. If needed, the dose may be increased to 10 mg solifenacin succinate once daily.
Do not exceed 5 mg tablet once daily in patients with:
- Severe Renal Impairment [Creatinine Clearance] (Clcr < 30 ml/min).
- Moderate Hepatic Impairment (Child-Pugh B)
- Concomitant Use Of Potent CYP3A4 Inhibitors
Use of UROCALM is not recommended in patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh C).
Method of administration
Solifenacin succinate should be taken orally and should be swallowed whole with liguids. It can be taken with or without food.
Contraindication
Solifenacin is contraindicated in patients with urinary retention, severe gastro-intestinal condition (including toxic megacolon), myasthenia gravis or narrow-angle glaucoma in patients who have demonstrated hypersensitivity to the drug.
Warnings and Precautions
Other causes of frequent urination (heart failure or renal disease) should he assessed before treatment with Solifenacin. If urinary tract infection is present, an appropriate antibacterial therapy should be started.
Solifenacin should be used with caution in patients with:
- Angioedema and anaphylactic reactions: Reports of angioedema of the face, lips and/or larynx, in some cases occurring after the first dose, have been described. Anaphylactic reactions have been reported rarely.
- Urinary Retention: Administer with caution to patients with clinically stenificant bladder outflow obstruction.
- Gastrointestinal Disorders: Use with caution in patients with decreased gastrointestinal motility.
- Central Nervous System Effects: Advise patients not to drive or onerate heavy machinery until they know how UROCALM affects them.
- Controlled Narrow-Angle Glaucoma: Use with caution in patients being treated for narrow-angle glaucoma.
- QT Prolongation: Use with caution in patients with a known history of QT prolongation or patients who are taking medications known to prolong the QT Interval.
- Dosed should not exceed 5mg for the patients with severe renal Impairment (creanine clearance ≤ 30 ml/min) moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh score of 7 to 9).
- Autonomic neuropathy.
Interactions with Other Medicaments
Drug Interactions
- Inhibitors of CYP3A4 may increase the concentration of UROCALM.
- Inducers of CYP3A4 may decrease the concentration of UROCALM.
Drugs Metabolized by Cytochrome P450
At therapeutic concentrations, solifenacin does not inhibit CYP1A1/2, 2C9, 2C19, 2D6, or 3A4 derived from human liver microsomes .
Pharmacological interactions
The therapeutic effect of Solifenacin may be reduced by concomitant administration of cholinergic receptor agonists.
An interval of approximately one week should be allowed after stopping treatment with Solifenacin, before commencing other anticholinergic therapy.
Solifenacin can reduce the effect of medicinal products that stimulate the motility of the gastro-intestinal tract, such as metoclopramide and cisapride.
Effect of other medicinal products on the pharmacokinetics of solifenacin
Solifenacin is metabolised by CYP3A4. Simultaneous administration of ketoconazole (200 mg/day),a potent CYP3A4 inhibitors resulted in two fold increase of the AUC of Solifenacin Therefore, the maximum dose of Solifenacin should be restricted to 5 mg, when used simultaneously with ketoconazole or therapeutic doses of other potent CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g. ritonavir, nelfinavir, itraconazole).
Simultaneous treatment of solifenacin and a potent CYP3A4 inhibitor is contra-indicated in patients with severe renal impairment or moderate hepatic impairment.
Effect of solifenacin on the pharmacokinetics of other medicinal products
Oral Contraceptives
Intake of Solifenacin showed no pharmacokinetic interaction of sollfenacin on combined oral contraceptives (ethinylestradiol/ levonorgestrel).
Warfarin
Intake of Solifenacin did not alter the pharmacokinetics of R-warfarin or S-warfarin or their effect on prothrombin time.
Digoxin
Intake of Solifenacin showed no effect on the pharmacokinetics of digoxin.
Pregnancy and Lactation
Pregnancy- Category C
The potential risk for humans is unknown. Caution should be exercised when prescribing to pregnant women.
Lactation
The use of Solifenacin should be avoided during breast-feeding.
Adverse drug reactions
Blurred vision, Dry mouth, constipation, Nausea, Dyspepsia and Abdominal pain, Urinary tract infection, Cystitis, Somnolence, Dysgeusia, Dizziness, Headache, Dry eyes, Nasal dryness, Gastrosophageal reflux diseases, Dry throat, Colonic obstruction, Faecal impaction, Vomiting, Dry skin, Prurities, Rash, Difficulty in micturition, Urinary retention, Fatigue Peripheral edema. This is not a complete list of ADR and others may occur.
Overdose and Treatment
Overdosage
Overdosage with solifenacin succinate can potentially result in severe anticholinergic effects.
Treatment
In the event of overdose with solifenacin succinate the patient should consult healthcare.
Storage
Store below 30°C. Protect from light and moisture.
Presentation
Blister Pack of 10 x10 Tablets.