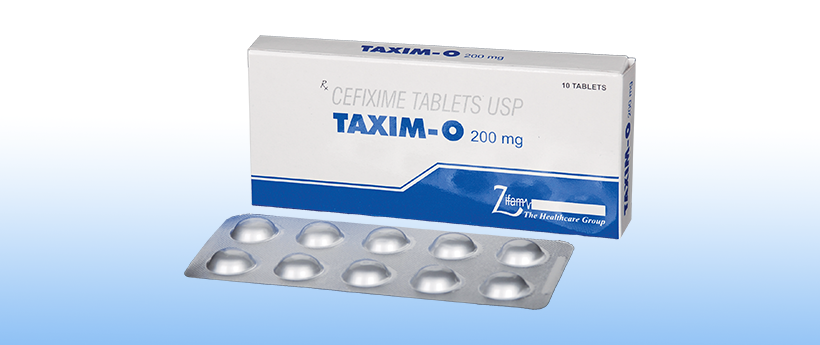
Taxim-O Tablets
- ENG
- မြန်မာ
FORMULATION:
TAXIM-O 200 mg
Each film coated tablet contains: 200 mg
Cefixime USP as Trihydrate equivalent to anhydrous Cefixime
Colour: Titanium Dioxide
PHARMACEURICAL FORM:
Film Coated Tablets
PHARMACOLOGICAL CLASSIFICATION:
ATC classification: J01DD08
Third-generation cephalosporins
PHARMACOLOGICAL ACTION:
Cefixime is an oral third generation cephalosporin which has marked in vitro bactericidal activity against a wide variety of Gram-positive and Gram-negative organisms.
Clinical efficacy has been demonstrated in infections caused by commonly occurring pathogens including Streptococcus pneumoniae, Streptococcus pyogenes, Escherichia coli, Proteus mirabilis, Klebsiella species, Haemophilus influenzae (beta-lactamase positive and negative), Branhamella catarhalis (beta-lactamase positive and negative) and Enterobacterspecies. It is highly stable in the presence of beta-lactamase enzymes.
Most strains of enterococci (Streptococcus faecalis, group D Streptococci) and Staphylococci (including coagulase positive and negative strains and methicillin-resistant strains) are resistant to cefixime. In addition, most strains of Pseudomonas, Bacteroides fragilis, Listeria monocytogenes and Clostridia are resistant to cefixime
PHARMACOKINETIC:
The absolute oral bioavailability of cefixime is in the range of 22-54%. Absorption is not significantly modified by the presence of food. Cefixime may therefore be given without regard to meals. From in vitro studies, serum or urine concentrations of 1. mcg/mL or greater were considered to be adequate for most common pathogens against which cefixime is active. Typically, the peak serum levels following the recommended adult or paediatric doses are between 1.5 and 3mcg/mL Little or no accumulation of cefixime occurs following multiple dosing.
The pharmacokinetics of cefixime in healthy elderly (age > 64 years) and young volunteers (11-35) compared the administration of 400 mg doses once daily for 5 days. Mean Cmax and AUC values were slightly greater in the elderly. Elderly patients may be given the same dose as the general population.
Cefixime is predominantly eliminated as unchanged drug in the urine. Glomerular filtration is considered the predominant mechanism. Metabolites of cefixime have not been isolated from human serum or urine. Serum protein binding is well characterized for human and animal sera; cefixime is almost exclusively bound to the albumin fraction, the mean free fraction being approximately 30%. Protein binding of cefixime is only concentration dependent in human serum at very high concentrations which are not seen following clinical dosing.
Transfer of 14C-labelled cefixime from lactating rats to their nursing offspring through breast milk was quantitatively small (approximately 1.5% of the mothers’ body content of cefixime In the pup). No data are available on secretion of cefixime in human breast milk. Placental transfer of cefixime was small in pregnant rats dosed with labelled cefixime.
INDICATION
- Upper Respiratory Tract Infection (URTI): e.g. otitis media: and other URTI where the causative organism is known or suspected to be resistant to other commonly used antibiotics, or where treatment failure may carry significant risk.
- Lower Respiratory Tract Infection (LRTI): e.g. bronchitis.
- Urinary Tract Infection: e.g. cystitis, cystourethritis, uncomplicated pyelonephritis.
Clinical efficacy has been demonstrated in infectious caused by commonly occurring pathogens including Streptococcus pneumoniae, Streptococcus pyogenes, Escherichia coli, Proteus mirabilis, Kliebsiella species, Haemophillus influenzae (beta-lactamase positive and negative), Branhamella catarrhalis (beta-lactamase positive and negative) and Enterobactor species. Cefixime is highly stable in the presence of beta-lactamase enzymes.
Most strains of enterococci (Streptococcus faecalis, group D Streptococci) and Staphylococci (including coagulase positive and negative strains and methicillin-resistant strains) are resistant to Cefixime. In addition, most strains of Pseudomonas, Bacteriodes fragalis, Listeria monocutogenes and Clostridia are resistant to Cefixime.
RECOMMENDED DOSE:
Route of Administration: Oral
Absorption of cefixime is not significantly modified by the presence of food. The usual course of treatment is 7 days
This may be continued for up to 14 days if required.
Adults and Children over 10 Years (Use cefixime tablet): The recommended adult dosage is 200-400 mg daily according to the severity of infection, given either as a single dose or in two divided doses.
The Elderly: Elderly patients may be given the same dose as recommended for adults. Renal function should be assessed and dosage should be adjusted in severe renal impairment’ (See “Dosage in Renal Impairment”).
Children: The recommended dosage for children is 8 mg/kg/day administered as single dose or in two divided doses. As general guide for prescribing in children the following daily doses in terms of volume of oral suspension are suggested:
| PatientWeight (kg) | Dose/Day (mg) | Cefixime 50rg/5mL Dose/Day (mL) |
| 5to7.5 | 50 | 5 |
| 7,6 to 10,5 | 75 | 7.5 |
| 10.6to 12.5 | 100 | 10 |
| 12.6to20.5 | 150 | 15 |
| 20.6to 28 | 200 | 20 |
Children weighing more than 45 kg or older than 12 years should be treated with the recommended adult dose (200-400 mg dally depending on the severity of Infection).
The safety and officacy of cefixime has not been established in children less than 6 months
Dosage in renal impairment: Cefixime may be administered in the presence of impaired renal function. Normal dose and schedule may be given in patients with creatinine clearances of 20 ml/min or greater. In patients whose creatinine clearance is less than 20 ml/min, it is recommended that a dose of 200 mg once daily should not be exceeded. The dose and regimen for patients who are maintained on chronic ambulatory peritoneal dialysis or hemodialysis should follow the same recommendation as that for patients with creatinine clearances of less than 20 ml/min.
Direction for Reconstitution:
Shake the bottle well to loosen the dry powder. Slowly add water provided with this pack up to the mark on the bottle and shake well. Add water if necessary, to adjust the volume up to the mark. After reconstitution keep the suspension in the refrigerator when not in use.
INTERACTIONS with other medicaments
Anticoagulants
In common with other cephalosporins, increases in prothrombin times have been noted in a few patients. Care should therefore be taken in patients receiving anticoagulants therapy.
Cefixime should be ad ministered with caution to patients receiving coumarin-type anticoagulants, e.g. warfarin potassium. Since cefixime may enhance effects of the anticoagulants, prolonged prothrombin time with or without bleeding may occur.
Other Forms of interaction
A false positive reaction of glucose in the urine may occur with Benedict’s or Fehling’s solution or with copper sulphate test tablets, but not with tests based on enzymatic glucose oxidase reactions.
A false positive direct Coombs test has been reported during treatment with cephalosporin antibiotics, therefore it should be recognized that a positive Coombs test may be due to the drug.
PREGNANCYAND LACTATION
Reproduction studies have been performed in mice and rats at doses up to 400 times the human dose and have revealed no evidence of impaired fertility or harm to the fetus due to cefixime. In the rabbit, at doses up to 4 times the human dose, there was no evidence of a teratogenic effect; there was a high incidence of abortion and maternal death which is an expected consequence of the known sensitivity of rabbits to antibiotic-induced changes in the population of the microflora of the intestine. There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Cefixime should therefore not be used in pregnancy or in nursing mothers unless considered essential by the physician.
CONTRA-INDICATIONS
Allergy to cephalosporins.Cefixime is contra-indicated in patients with renal impariment with a creatinine clearance below 60ml/min.
Adverse Effects
Gastrointestinal Disturbances: The most frequent side effects seen with Cefixime are diarrhoea and stool changes. Moderate to severe diarrhoea has been reported. Other gastrointestinal side effects seen less frequently are nausea, abdominal pain dyspepsia, vomiting and flatulence. Pseudomembranous colitis has been reported.
AVAILABILITY
1 x 10’s Blister
10 x 10’s Blister
Updated on 9th Feb 2024