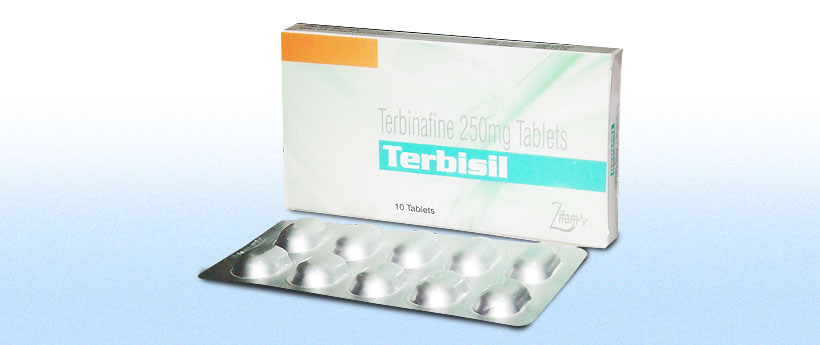
Terbisil
- ENG
- မြန်မာ
COMPOSITION
Each uncoated tablet contains:
Terbinafine Hydrochloride BP
Equivalent to Terbinafine 250mg
Description
Terbinafine is an allylamine having a broad-spectrum of antifungal activity. At low concentrations terbinafine is antifungal against dermatophytes, moulds and certain dimorphic fungi. The activity against yeasts is fungicidal or fungistatic depending on the species.
Terbinfaine interferes selective with fungal sterol biosynthesis at an early stage. This leads to a deficiency of ergosterole and to an intracellular accumulation of squalene in the fungal cell membrane. Both the deficiency in ergosterol and the accumulation of squalene are responsible for fungal cell death. Terbinafine also acts by inhibition of squaleneepoxidase in the fungal cell membrane. When given orally, the active substance concentrates in skin, hair and nails, at levels associated with fungicidal activity..
INDICATIONS
Treatment of fungal infections sensitive to terbinafine such as Tineacorporis, Tineacruris and Tineapedis (caused by dermatophytes) if considered appropriate due to the site, severity or extent of the infection.
The treatment of onychomycosis (terbinafine-sensitive fungal infection of the nails) caused by dermatophytes.
N.B Orally administered terbinafine tablets are not effective aginstPityriasisversicolor. The official local guidelines should be borne in mind, for example, national recommendations relating to the correct use and prescription of antimicrobial drugs.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Hypersensitivity to terbinafine or to any of the excipients.
Severe renal impairment.
Severe hepatic impairment.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
The plasma clearance of terbinafine may be accelerated by active substances which induce metabolism (such as rifampicin) and may be inhibited by active substances which inhibit cytochrome (such as cimetidine).
DOSAGE:
Route of administration: Oral use
The duration of treatment depends on the indication and the degree of severity of the infection.
Adults: 250 mg once daily.
Patients with impaired renal function (creatinine clearance less than 50ml/min or serum creatinineof more than 300 micromol/l) should be treated with half of the normal dose.
Skin Infections:
The likely duration of treatment for Tineapedis, Tineacorporis and Tineacruris is 2 to 4 weeks.
For Tineapedis (interdigital, plantar/moccasin-type): recommended treatment periods may be upto 6 weeks.
Complete disappearance of the symptoms of the infection may not occur until several weeks after mycological cure.
Onychomycosis
In most patients the duration of successful treatment is 6 to 12 weeks.
Fingernail onychomycosis:
In most cases 6 weeks’ treatment is sufficient in fingernail onychomycosis.
Toenail onychomycosis:
In most cases 12 weeks’ treatment is sufficient in toenail onychomycosis although a few patients may require treatment up to 6 months.
Poor nail out growth during the first weeks of treatment may enable identification of those patients in whom longer therapy is required. Complete resolution of signs and symptoms of infection may not occur until several weeks after mycological cure and i s only seen several months after stopping treatment, which is the time for growth of healthy nail.
Children and adolescents (<18 years)
There is limited experience with oral terbinafine in children and adolescents and therefore its use cannot be recommended.
Use in elderly
There is no evidence to suggest that elderly patients require different dosages.
PREGNANCY & LACTATION
Foetal toxicity and fertility studies in animals suggest no undesirable effects.
Pregnancy:
There is no clinical experience with terbinafine in pregnant women. Terbinafine should not be administered during pregnancy unless clearly necessary.
Lactation:
Terbinafine is excreted in breast milk and therefore, nursing mothers should not be given terbinafine whilst breast feeding. Breast-feeding should be discontinued before starting the treatment with terbinafine tablets.
OVERDOSAGE
Few cases of overdose (up to 5 g) have been reported. The symptoms are headache, nausea, epigastric pain and dizziness.
The recommended treatment is elimination of the active substance, primarily by use of active charcoal and symptomatic treatment.
ADVERSE EFFECTS
The adverse reactions are usually mild to moderate and transient.
Blood and lymphatic system disorders:
Very rare (<1/10,000 inclusive isolated reports): Haematologicaldistrubances such as neutropenia, agranulocytosis and thrombocytopenia.
Immune system disorders
Very rare (<1/10,000): Manifestation or aggravation of cutaneous or systemic lupus erythematosus.
Very rare (< 1/10,000 including isolated reports ): Anaphylactic reactions.
Psychiatirc disorders
Very rare (< 1/10,000 including isolated reports): Psychiatirc disturbances such as depression and anxiety.
Nervous system disorders
Common (> 1/100, <1/10): Headache.
Gastrointestinal disorders:
Common (>1/1000 and <1/10): Gastrointestinal symptoms (feeling of fullness, loss of appetite, dyspepsia, nausea, mild abdominal pain, diarrhoea).
Uncommon (>1/1000 and <1/100): Taste disturbances, including loss of taste, that usually revert several weeks after withdrawal of the active substance. Isolated cases of persistent taste disturbances have been reported. In very few severe cases, a reduced intake of food causing significant loss of weight has been seen.
Hepatobiliary disorders:
Rare (>1/10,000 and <1/1000): Hepatobiliarydysfuntion (primarily of choldstatic type).
Very rare (<1/10,000 inclusive isolated reports): Severe hepatic failure.
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders:
Common (> 1/100 and<1/10): Non-serious skin reactions (rash, urticaria).
Rare (>1/10.000 and <1/1000): Severe skin reactions (e.g. Stevens-Johnsons syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, photosensitivity) and anaphylactoid reactions (incl. angioedema). If progressive rash occurs, the treatment with terbinafine should be discontinued.
Very rare (<1/1,000 including isolated reports ): Exacerbation of psoriasis ,loss of hair.
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders:
Rare (>1/10,000 and <1/1000): Arthralgia and myalgia. These may occur as part of a hypersensitivity reaction in association with allergic skin reactions.
PRESENTATION
Terbisil Tablet -10 Tablets in alualu blister and 1 blister packed in a pre printed carton.