TCL 0.5
- ENG
- မြန်မာ
TCL 0.5 (TACROLIMUS CAPSULES USP 0.5 MG)
Each hard gelatin capsule contains:
Tacrolimus Monohydrate USP
Equivalent to Tacrolimus 0.5 mg
Excipients: q.s.
Approved colour used in capsule shell
Each hard gelatin capsule contains:
Tacrolimus Monohydrate USP
Equivalent to Tacrolimus 1.0 mg
Excipients: q.s. Approved colour used in capsule shell
Each hard gelatin capsule contains:
Tacrolimus Monohydrate USP
Equivalent to Tacrolimus 5.0 mg
Excipients: q.s.
Approved colour used in capsule shell
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
TCL (tacrolimus) is a calcineurin-inhibitor immunosuppressant indicated for
• Prophylaxis of organ rejection in patients receiving allogeneic liver, kidney or heart transplants
• Use concomitantly with adrenal corticosteroids; in kidney and heart transplant, use in conjunction with azathioprine or mycophenolate mofetil (MMF)
PHARMACOKINETICS
Absorption
Absorption of tacrolimus from the gastrointestinal tract after oral administration is incomplete and variable. The absolute bioavailability of tacrolimus was 17 + 10% in adult kidney
transplant patients (N = 26), 22 $ 6% in adult liver transplant
patients (N = 17), 23 ‡ 9% in adult heart transplant patients (N =
11) and 18 ‡ 5% in healthy volunteers (N = 16).
Tacrolimus maximum blood concentrations (Cmax ) and area under the curve (AUC) appeared to increase in a dose-proportional fashion in 18 fasted healthy volunteers receiving a single oral dose of 3, 7, and 10 mg.
If pediatric patients are converted between formulations, therapeutic drug monitoring must be performed and dose adjustments made to ensure that systemic exposure to tacrolimus is maintained.
The rate and extent of tacrolimus absorption were greatest under fasted conditions. The presence and composition of food decreased both the rate and extent of tacrolimus absorption when administered to 15 healthy volunteers.
Distribution
The plasma protein binding of tacrolimus is approximately 99% and is independent of concentration over a range of 5-50 ng/mL.
Tacrolimus is bound mainly to albumin and alpha-1-acid glycoprotein, and has a high level of association with erythrocytes.
The distribution of tacrolimus between whole blood and plasma depends on several factors, such as hematocrit, temperature at the time of plasma separation, drug concentration, and plasma protein concentration.
Metabolism
Tacrolimus is extensively metabolized by the mixed-function oxidase system, primarily the cytochrome P-450 system (CYP3A). A metabolic pathway leading to the formation of 8 possible metabolites has been proposed. Demethylation and hydroxylation were identified as the primary mechanisms of biotransformation in vitro. The major metabolite identified in incubations with human liver microsomes is 13-demethyl tacrolimus. In in vitro studies, a 31-demethyl metabolite has been reported to have the same activity as tacrolimus.
Excretion
The mean clearance following IV administration of tacrolimus is 0.040, 0.083, 0.053, and 0.051 L/hr/kg in healthy volunteers, adult kidney transplant patients, adult liver transplant patients, and adult heart transplant patients, respectively.
In man, less than 1% of the dose administered is excreted unchanged in urine.
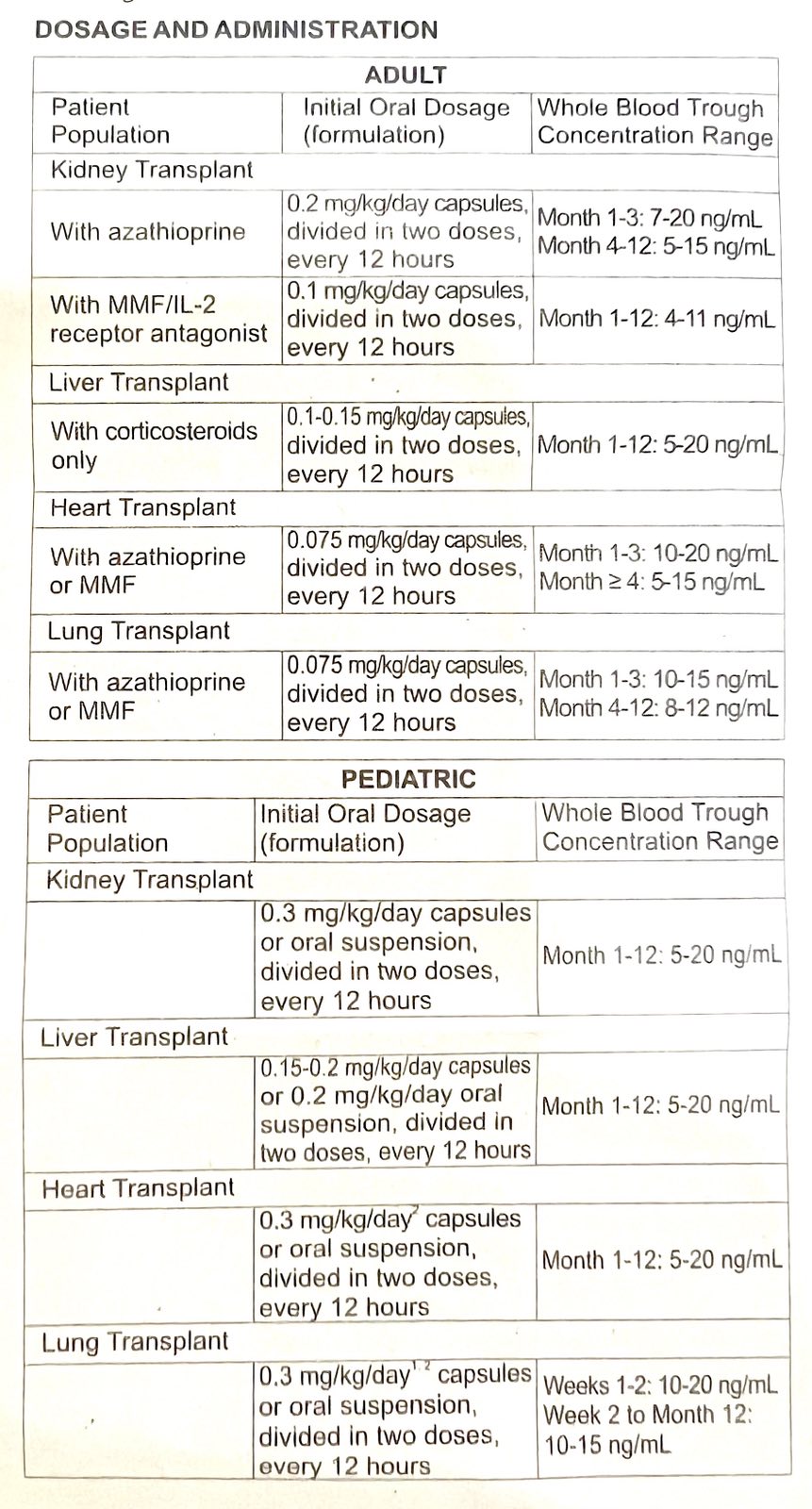
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
• Careful and frequent monitoring of tacrolimus trough concentrations is recommended; Black patients may require higher doses in order to achieve comparable trough concentrations
• Hepatic/Renal impaired patients should receive doses at the lowest value of the recommended initial oral dosing range
• Administer capsules consistently with or without food; do not drink grapefruit juice.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
• Hypersensitivity to tacrolimus or HCO-60 (polyoxyl 60 hydrogenated castor oil)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
• Malignancies And Serious Infections: Increased risk for developing serious infections and malignancies with TCL or other immunosuppressants that may lead to hospitalization or death.
• Not Interchangeable with Extended-Release Tacrolimus
Products – Medication Errors: Instruct patients or caregivers to recognize the appearance of TCL capsules.
• New Onset Diabetes After Transplant: Monitor blood glucose
• Nephrotoxicity: Acute and/or chronic; reduce the dose; use caution with other nephrotoxic drugs
• Neurotoxicity: Risk of Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome, monitor for neurologic abnormalities; reduce or discontinue TCL (tacrolimus) and other immunosuppressants
• Hyperkalemia: Monitor serum potassium levels. Careful consideration should be given prior to use of other agents also associated with hyperkalemia
• Hypertension: May require antihypertensive therapy. Monitor relevant drug-drug interactions
• Use with Sirolimus: Not recommended in liver and heart transplant due to increased risk of serious adverse reactions
• Myocardial Hypertrophy: Consider dosage reduction or discontinuation
• Immunizations: Use of live vaccines should be avoided
• Pure Red Cell Aplasia: Discontinuation should be considered
ADVERSE REACTIONS
• Kidney Transplant: The most common adverse reactions (≥ 30%) were infection, tremor, hypertension, abnormal renal function, constipation, diarrhea, headache, abdominal pain, insomnia, nausea, hypomagnesemia, urinary tract infection, hypophosphatemia, peripheral edema, asthenia, pain, hyperlipidemia, hyperkalemia, anemia
• Liver Transplant: The most common adverse reactions (2 40%) were tremor, headache, diarrhea, hypertension, nausea, abnormal renal function, abdominal pain, insomnia, paresthesia, anemia, pain, fever, asthenia, hyperkalemia, hypomagnesemia, and hyperglycemia
• Heart Transplant: The most common adverse reactions ( ≥ 15%) were abnormal renal function, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, CMV infection, tremor, hyperglycemia, leukopenia, infection, anemia, bronchitis, pericardial effusion, urinary tract infection and hyperlipemia
DRUG INTERACTIONS
• Mycophenolic Acid Products: Can increase MPA exposure after crossover from cyclosporine to TCL (tacrolimus); monitor for MPA-related adverse reactions and adjust MMF or MPA-dose as needed
• Nelfinavir and Grapefruit Juice: Increased tacrolimus concentrations via CYP3A inhibition; avoid concomitant use
• CYP3 Inhibitors: Increased tacrolimus concentrations; monitor concentrations and adjust tacrolimus dose as needed with concomitant use
• CYP3A4 Inducers: Decreased tacrolimus concentrations; monitor concentrations and adjust tacrolimus dose as needed with concomitant use
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
• Pregnancy: Tacrolimus can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Data from postmarketing surveillance and TPRI suggest that infants exposed to tacrolimus in utero are at a risk of prematurity, birth defects/congenital anomalies, low birth weight, and fetal distress. Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to the fetus.
• Lactation: Controlled lactation studies have not been conducted in humans; however, tacrolimus has been reported to be present in human milk. The effects of tacrolimus on the breastfed infant, or on milk production have not been assessed. Tacrolimus is excreted in rat milk and in peri-/postnatal rat studies; exposure to tacrolimus during the postnatal period was associated with developmental toxicity in the offspring at clinically relevant doses.
The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for
TCL and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from TCL or from the underlying maternal condition.
• Renal impaired: The pharmacokinetics of TCL in patients with renal impairment was similar to that in healthy volunteers with normal renal function. However, consideration should be given to dosing TCL at the lower end of the therapeutic dosing range in patients who have received a liver or heart transplant and have pre-existing renal impairment.
Hepatic Impairment: The mean clearance of tacrolimus was substantially lower in patients with severe hepatic impairment (mean Child-Pugh score: > 10) compared to healthy volunteers with normal hepatic function. Close monitoring of tacrolimus trough concentrations is warranted in patients with hepatic impairment.
STORE AND DISPENSE
STORAGE: Store in a cool and dry place below 30°C.
Protect from light and moisture.
Keep Medicine away from children.
SHELF LIFE: 24 months.
PACK SIZE: Blister pack of 10 capsules.