Trela
- ENG
- မြန်မာ
Composition:
Trela 50 Tablet: Each film-coated tablet contains Trelagliptin Succinate 66.5 mg equivalent to Trelagliptin 50 mg
Trela 100 Tablet: Each film-coated tablet contains Trelagliptin Succinate 133 mg equivalent to Trelagliptin 50 mg
Therapeutic Class: Anti-Diabetic Drug
PHARMACOLOGICAL ACTION
Mechanism of Action
By inhibiting the activity of dipeptidyl peptidase DPP-4 which inactivates glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) from secretion from the intestines to the blood via stimulation from oral intake of food, increases GLP-1 blood concentration and promotes blood glucose concentration-dependent insulin secretion from the pancreas.
1. DPP-4 Inhibition
a) Selectively inhibits human plasma DPP-4 activity (IC50 value: 4.2 mol/L) (in vitro).
Moreover, when IC50 value (nmol/ L) was compared under similar conditions (in vitro) in order to compare Trelagliptin and alogliptin DPP-4 inhibitory action, values were 1.3 and 5.3 respectively.
b) Type 2 diabetes patients who exhibit insufficient blood glucose control through dietary and exercise measures were given 100 mg of Trelagliptin (once weekly, before meal) for 12 weeks. The results of the double blind, parallel group, placebo-controlied comparative study show that 7 days after final treatment, the average DPP-4 inhibition rate was 77.4% compared in the Trelagliptin 100 mg group.
3. Glucose Tolerance Improvement
A single, oral dose of Trelagliplin was given to obese type 2 diabetic model organisms (Wister fatty rat) and non-obese type 2 diabetic model organisms (N-STZ-1.5 rat) after 1 night of fasting, Glucose was then given orally 1 hour after drug administration to conduct a glucose load test. Results from the tests revealed a glucose tolerance-improving action.
PHARMACOKINETICS
1. Blood concentration
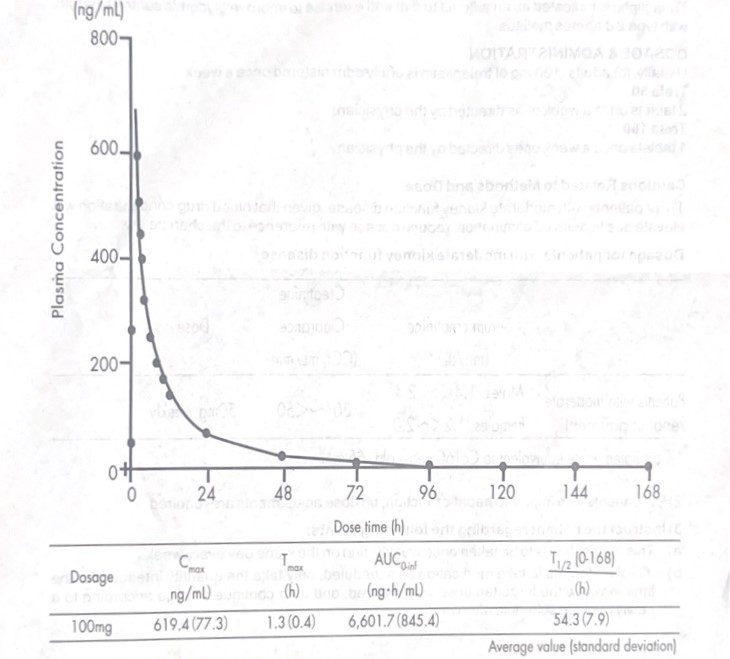
a) Single Dose
Healthy adults (8) were given Trelagliptin 100 mg 30 minutes before meal, resulting in the following single dose blood serum concentration and pharmacological parameters. 168 hours after administration, serum blood concentration was an average of 2.1 ng/mL.
b) Repeated Dose
Healthy adults (9) were given Trelagliptin at 100 mg 30 minutes before meal once daily. Alter 3 days, once daily repeat dosages were given 30 minutes before meal for 11 days. Day-1 Cmax and AUC on, were 544.3 (122.0) ng/mL and 5,572.3 (793.2) ng-h/mL respectively. Day-14 Ca and AUC (vam) average values (standard deviation) were 602.6 (149.5) ng/mL and 5,292.9 (613.8 )ng-h/mL respectively.
(Approved administration and dosage for this drug consists of normally, 100 mg of Trelagliptin is administered to adults once weekly by mouth).
c) Dietary effects
Healthy adults (12) were given Trelagliptin at 100 mg 30 minutes before meal, resulting in a max and AUC (0) 16.8% and 2.5% greater compared to fasting administration, respectively.
2. Plasma Protein Binding Rate
Trelagliptin at a concentration of 0.1~10ug/mL was added to human plasma, resulting in a plasma protein binding rate of 22.1-27.6% (in vitro).
3. Metabolism
a) Trelagliptin is metabolized mainly by CYP2D6 N -demethylation from the active metabolite
M-1. Moreover, human plasma metabolite M-1 consisted of less than 1% unaltered Trelagliptin.
b) Trelagliptin demonstrates weak inhibition of CYP3A4/5.
However, (direct inhibitory action IC50 value: 100 umol/L or more, metabolic inhibitory action IC50 value: 12umol/ (L midazolam 1′-hydroxylation activity) and 28umol/ L testosterone 6 B-hydroxylation activity), CYP1A2, CYP2B6, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C19 and CYP2D6 were not inhibited, and CYP1A2, CYP2B6, and CYP3A4 were not induced (in vitro).
4. Elimination
a) Healthy adults (12) were given a single dose of Trelagliptin 100 mg in a fasted state or 30 minutes after the start of meal. Trelagliptin accumulation in the urine AUC were 76.6 % and 76.1% respectively 168 hours alter administration.
b) Trelagliplin is a P-glycoprotein substrate and sightly inhibits digoxin infusion via P-glycoprotein action (IC50:500pmol/L or more). Moreover, Trelagliptin demonstrates inhibitory action on organiccation transporter OCT2 involved with metformin processing (IC50 value: 55.9mol/I) (in vitro).
5. Action with Kidney Disease
Individuals with kidney disease and healthy adults were given a single dose of Trelagliplin at 50 mg, resulting in the following AUC (0-tlac) and Cmax values. When compared to healthy adults with respect to age, gender, ethnicity, and body weight, individuals with kidney disease (C=50-80mL/ min, 6 cases) showed a 55.7% increase, 36.3% increase, patients with moderate kidney function disorder (Ca=30-50mL/min, 6 cases) showed 105.7% increase, 12.9% increase, patients with severe kidney function disorder (C. <30mL/min, 6 cases) showed 201.4% increase, 9.1% increase, end stage kidney disease patients (6 cases) showed 268.1% increase, 13.8% reduction. Moreover, 9.2% of the Trelagliptin dosage was removed after 4 hours of dialysis.
Approved administration and dosage for this drug consists of normally, 100 mg of Trelagliptin is administered to adults once weekly by mouth.
6. Activity with Liver Disease
Individuals with moderate liver disease (Child-Pugh score of 7-9, 8 cases) and healthy adults (8 were given a single dose of Trelagliplin at 50 mg, resulting in the following AUC in and Cmat values. When compared to healthy adults with respect to age, gender, ethnicity, smoking, and body weight, AUC (an increased 5.1% and Cm increased 4.3 %.
INDICATION
Trelagliptin is indicated as an adjunct to diet and exercise to improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION
Usually, for adults, 100 mg of trelagliptin is orally administered once a week.
Trela 50
2 tablets once a week or as directed by the physician.
Trela 100
1 tablet once a week or as directed by the physician.
Cautions Related to Methods and Dose
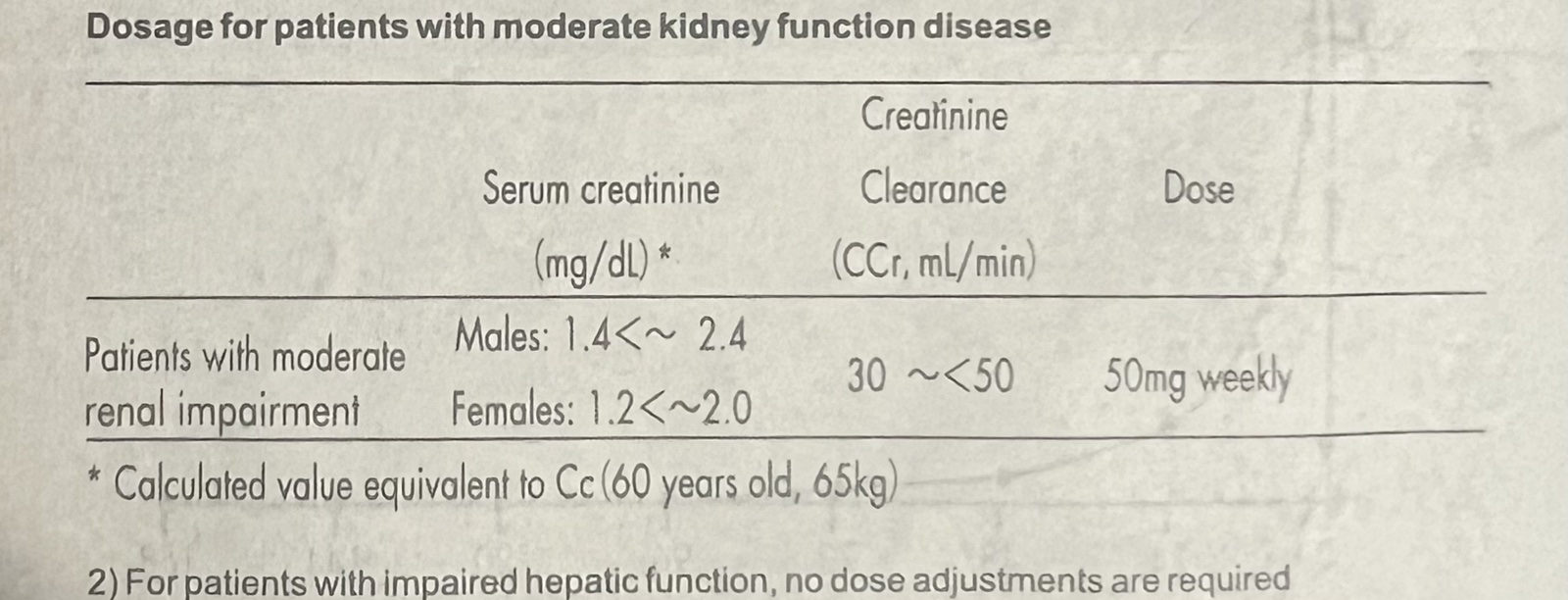
1) For patients with moderate kidney function disease, given that blood drug concentration will elevate due to delayed elimination, reduce dosage with reference to the chart below.
Dosage for patients with moderate kidney function disease
2) For patients with impaired hepatic function, no dose adjustments are required
3) Instruct the patient regarding the following points:
a) This medication is to be taken once weekly, and on the same day every week.
b) If patient forgets to take medication as scheduled, only take the quantity intended for the time in which the forgotten dose was realized, and then continue dosage according to a newly decided schedule afterwards.
WARNINGS
Provide cautious dosage to the following patients or circumstances.
1) Patients with moderate kidney function disorder
2) Patients undergoing treatment with sulfonylurea drugs or insulin medication [there are reports of severe hypoglycemia with use in combination with other DPP-4 inhibitors]
3) Hypopituitarism or hypoadrenalism
4) Malnutrition, starvation, irregular eating patterns, in sufficient eating, or hyposthenia
5) Vigorous exercise
6) Patients who consume excessive alcohol
Major Warnings
1) This drug may cause hypoglycemia when used in combination with other diabetes medications, so thoroughly explain and caution the patient of such risks of hypoglycemia when combining with other medications. There is an increased risk of hypoglycemia particularly when combined with sulfonylurea drugs and insulin medications. Consider reducing the dose of sulfonylurea drugs or insulin medication when used in combination with these drugs in order to lessen the risk of hypoglycemia.
2) This drug is to be taken orally once per week. Effects may persist even alter dosage is ceased, so take sufficient notice of blood sugar values and side effects. Moreover, evaluate the starting period and dose based on the state of blood sugar management when using other diabetes medications after cessation of this medication.
3) Only consider application for patients with established diagnosis of diabetes mellitus. Pay attention to conditions that show abnormal sugar resistance, glucosuria and other symptoms resembling diabetes (renal glucosuria thyroid function abnormality, etc.)
4) Application of this drug should only be considered once diet- and exercise-based diabetes treatments have already been implemented with unsatisfactory results.
5) During administration of this drug, progress should be sufficiently observed along with quantitative blood sugar measurements. If no results are seen after 2 to 3 months of treatment, consider changing to a more appropriate treatment method.
6) During dosage maintenance, the medication may no longer become necessary, or the effects of the drug may diminish due to complications with poor nutrition or infectious disease. In such cases, evaluate continuation of normal dose, medication selection, etc. upon consideration of dietary volume, blood sugar levels, and presence of infectious symptoms.
7) Warn patients that work in high places, operate machinery, etc., as low blood sugar can occur.
8) Clinical results and safety regarding combination with insulin medication has not been investigated.
9) This drug and GLP-1 receptor agonists both possess the ability to lower blood sugar and assist GLP-1 receptor agonists. There are no clinical study results regarding the combination of these medications, and neither the efficacy nor the safety can be confirmed.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Glimepiride
When 200 mg of trelagliptin was repeatedly administered to 12 healthy adults once daily for 11 days and was co-administered with 1 mg of glimepiride in a single dose on day 11 of trelagliptin administration, the point estimates [two-sided 90% confidence interval] of the least squares mean ratios of AUCo and Cmax of glimepiride co-administered with trelagliptin were 103.5% [99.1, 108.1] and 121.5% [109.6, 134.81, respectively, compared with glimepiride alone.
Metformin
When 100 mg of trelagliptin once daily and 1000 mg of metformin twice daily were repeatedly administered for 12 days to 48 healthy adults (crossover study), the point estimates [two-sided 90% confidence intervalj of the least squares mean ratios of AUC, and Can of trelagliptin co-administered with metformin were 105.0% [102.3, 107.8] and 108.5% [100.6, 117.0] compared with trelagliptin alone. The point estimates [two-sided 90% confidence interval] of the least squares mean ratios of AUC, and max of metformin co-administered with trelagliptin were 90.4% [84.1, 97.2] and 73.3% (66.6, 80.61, compared with metformin alone.
Caffeine, Tolbutamide, Dextromethorphan, Midazolam
When 100 mg of trelagliptin was repeatedly administered once daily for 11 days to 18 healthy adults and was co-administered with drug cocktail (200 mg of caffeine, 500 mg of tolbutamide, 30 mg of dextromethorphan, and 4 mg of midazolam) in a single dose on day 11, the two-sided
90% confidence intervals of the least squares mean ratios of caffeine,
tolbutamide, midazolam, and respective metabolites co-administered with trelagliptin were within the range between 80% and 125% compared with drug cocktail alone. The point estimates [two-sided 90% confidence interval] of the least squares mean ratios of AUCt and Cmux Of dextromethorphan co-administered with trelagliptin were 117.9% [98.8, 140.7) and 111.3% [95.5, 129.8], while the two-sided 90% confidence intervals of the least squares mean ratios of AUCIns and Cmax of a metabolite dextrophan were within the range between 80% and 125%.
No clinically meaningful interactions (with both drug and food were observed, and no need for dose adjustment of trelagliptin or other concomitantly administered drugs was identified.
Trelagliptin is primarily renally excreted. Cytochrome (CYP) P450-related metabolism is negligible. No significant drug-drug interactions were observed with the CYP-substrates tested.
CONTRAINDICATIONS:
Hypersensitivity to trelagliptin or any of its components
• Patients with severe renal impairment or end-stage renal failure on dialysis
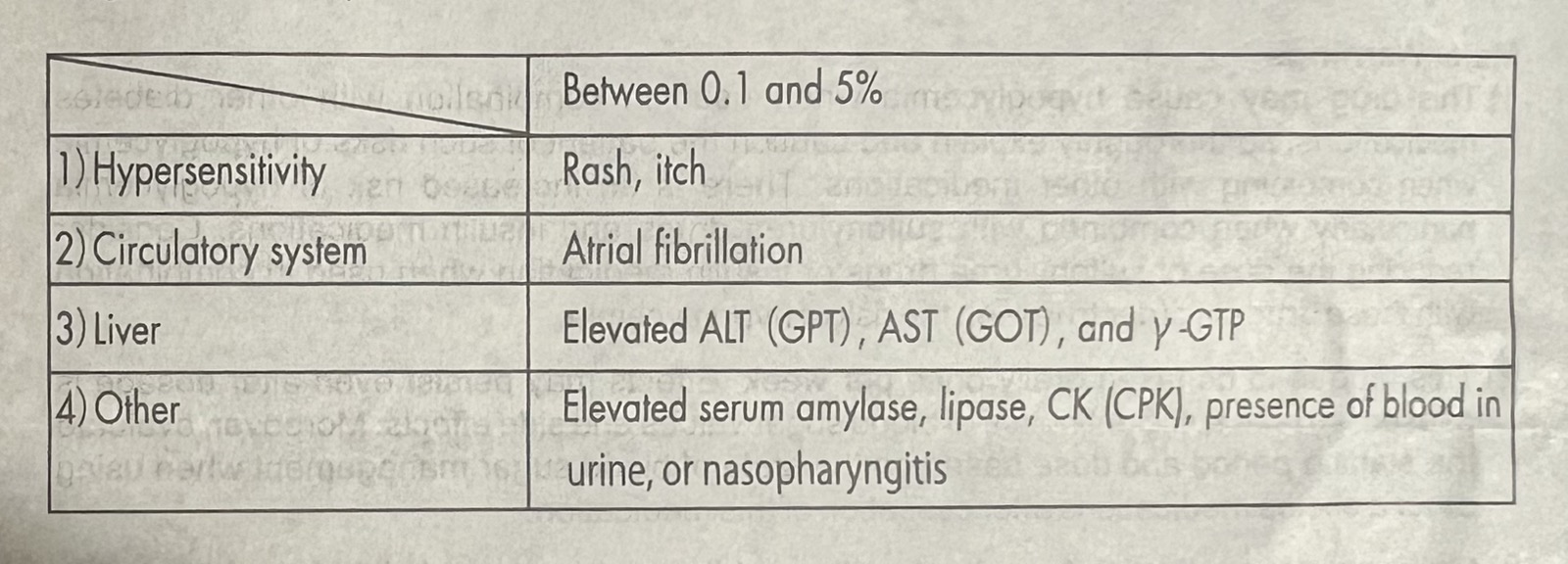
UNDESIRABLE EFFECTS
Clinical trial data for expected adverse events is based on pooled safety analysis from the following studies: two controlled studies with type 2 diabetes (N= 51 for trelagliptin 50 mg and N= 55 for trelagliptin 100 mg and N=101 for trelagliptin 100 mg) and other two main studies with type 2 diabetes (N=680 for trelagliptin 100 mg and N=14 for trelagliptin 100 mg). Adverse drug reactions are presented in table below.
SPECIAL WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Acute pancreatitis has been associated with other DPP-4 inhibitors. Acute pancreatitis can occur, so careful observation is called for and sustained, intense abdominal pain, vomiting, and other abnormal symptoms should be followed up with cessation of the drug followed by appropriate measures.
SPECIAL PATIENT POPULATION
1. Administration to Elderly Patients: Since many geriatric patients generally have lowered kidney function, take note of side effects and administer a cautious dose while sufficiently observing treatment progress.
2. Administration to pregnant women, lactating women, or for gynecological use
a) For women who are pregnant or may be pregnant, only administer drug upon fully evaluating the risks and benefits of treatment. The safety of use during pregnancy is not established. There are reports of the drug crossing the placenta in animal (rat) tests.
b) Avoid giving drug to women who are breastfeeding and stop breastfeeding if drug must be administered.
3. Administration to children: The safety of this drug in infants with low birth weight, newbor infants, nursing infants, babies, and children is not established.
OVERDOSE
1. Overdose safety information regarding overdose has not been sufficiently collected, for dietary and exercise treatments, as well as metformin-only treatments, or for type 2 diabetes patients in which blood sugar control is not ideal. However, there have been overseas studies in which 100 mg of this drug was taken orally every day over 12 consecutive weeks and side effects did not differ from the placebo group.
2. Overseas clinical studies involving single Trelagliptin doses of 800 mg reported QT elongation.
PHARMACEUTICAL INFORMATION
Storage conditions
Store In a cool and dry place below 30°C.
Protect from light and moisture.
Keep medicine away from children.
SHELF LIFE: 24 months.
PACK SIZE: Blister pack of 4 tablets.